Selecting Better Leaders
How to Use the LSP-R Selection Report
Last year SIGMA introduced the Leadership Skills Profile-Revised (LSP-R), a personality-based assessment that predicts leaders’ expected level of performance on up to 50 different competencies. There are a number of ways the LSP-R can be leveraged to strengthen your organization’s leadership team. Here, we discuss how the LSP-R Selection Report can be used to help your organization select better leaders.
A strong case can be made for adding a personality assessment to your organization’s selection process. When used in combination with other selection tools such as interviews, assessment centers, and cognitive ability, personality has been shown to be an important predictor of job performance. The LSP-R is a great option for those looking to hire top performing leaders and executives, and the Selection Report provides a concise, easy to interpret report for streamlining hiring decisions. Below we outline some key guidelines to help you make the most of the LSP-R Selection Report.
Look for Broad Patterns of Fit
The LSP-R Selection Report provides summary scores for Overall Expected Performance, Interpersonal Leadership Effectiveness, and Task Orientation. These are broad indices of performance that provide an at-a-glance assessment of critical aspects of leadership for each candidate.
- Overall Expected Performance is an index of performance based on the average of the candidate’s scores on all LSP-R competencies.
- Interpersonal Leadership Effectiveness is an index of a candidate’s competence in communicating and interacting with others.
- Task Orientation reflects competence related to timely and effective goal-setting and task management.
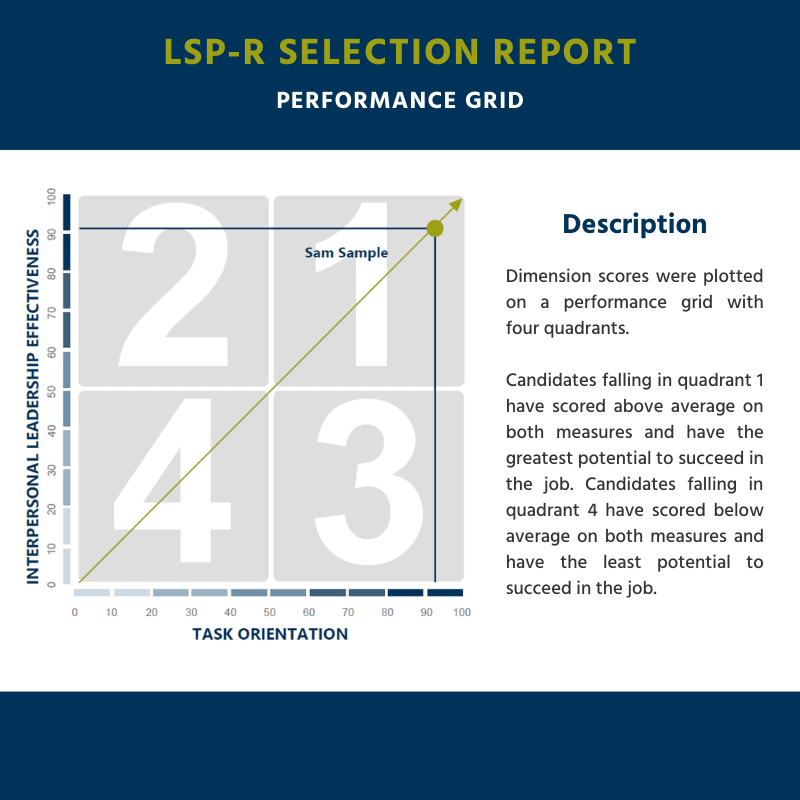
These summary scores are a convenient way to compare candidates at a high level. Although the Overall Expected Performance scores are useful for putting together an initial ranking of candidates, the LSP-R Selection Report’s Performance Grid provides additional nuance to these comparisons. The Performance Grid categorizes candidates scores based on two criteria: their Interpersonal Leadership Effectiveness Score and their Task Orientation score. Depending on whether the candidate has scored above or below average on these metrics, as compared to other leaders, they will be placed into one of four performance quadrants. A description of the candidate’s quadrant classification is also provided to help you interpret their results.
Match Position Requirements to Specific Competencies
After reviewing candidates’ summary scores, expected performance on individual competencies can be used to further differentiate candidates. Matching specific competencies assessed by the LSP-R to position requirements can be done with a job analysis, which should be an important part of your selection process. We recommend you match the competencies assessed by the LSP-R to the essential tasks and responsibilities of the position, as well as the critical knowledge, skills, abilities, and other characteristics (KSAOs) that an individual needs to perform the job. Matching position requirements to specific competencies can help you hone in on important differences between candidates that might not be readily apparent from their summary scores.
Integrate the Report into Your Current Procedures
A good selection procedure relies on multiple sources of information to increase the accuracy of final decisions. These procedures might include evaluating resumes, conducting interviews, and administering work samples or other assessments. The LSP-R Selection Report is best employed when integrated into the procedures for selection already in place at your organization.
The LSP-R comprehensively assesses several critical leadership competencies, making it a powerful tool for distinguishing between candidates. However, this also has the potential to result in an overwhelming amount of information to consider if used early in the selection process when you have a large pool of candidates. Therefore, we recommend that you use the LSP-R Selection Report after the initial applicant pool has been narrowed to your top candidates.
For example, you might want to reduce your initial candidate pool by evaluating all resumes and administering other assessments such as measures of cognitive ability or employee behavior. Then, the LSP-R Selection Report can be used in conjunction with selection tools that require a greater time investment, such as interviews and work samples. In this way the LSP-R Selection Report can help to inform the decisions you make from these other tools.
Looking Forward with LSP-R
Whomever you choose for the role, we recommend you retain copies of their LSP-R results. When it comes time for the individual’s annual performance review, it can be helpful to look back at their LSP-R results to help evaluate the effectiveness of your selection procedures. In addition, these results can serve as a strong foundation for future leader development plan. You may wish to administer a 360 degree feedback tool, like SIGMARadius, to assess the progress the individual has made on key competencies since being hired. By collecting data from colleagues, supervisors, and direct reports you can more holistically evaluate the effectiveness of your selection procedures, and begin to identify future development opportunities for your leaders.
Getting Started
When used appropriately, the LSP-R Selection Report can be an invaluable tool that helps you make better hiring and placement decisions. If you’d like some help integrating the LSP-R and any of its reporting features, like the Selection Report, into your organization, we’d be happy to help.